exposition - noun (music) the section of a movement (especially in sonata form) where the major musical themes first occur; an account that sets forth the meaning or intent of a writing or discourse; a systematic interpretation or explanation (usually written) of a specific topic; a collection of things (goods or works of art etc.) for public display
expressionism - noun an art movement early in the 20th century; the artist's subjective expression of inner experiences was emphasized; an inner feeling was expressed through a distorted rendition of reality
fable - noun a short moral story (often with animal characters); a story about mythical or supernatural beings or events; a deliberately false or improbable account
fallacy - noun a misconception resulting from incorrect reasoning
falling - adj. becoming lower or less in degree or value; decreasing in amount or degree; coming down freely under the influence of gravity
action - noun something done (usually as opposed to something said); the most important or interesting work or activity in a specific area or field
farce - noun a comedy characterized by broad satire and improbable situations
figurative - adj. (used of the meanings of words or text) not literal; using figures of speech; consisting of or forming human or animal figures
language - noun the mental faculty or power of vocal communication; a systematic means of communicating by the use of sounds or conventional symbols; the cognitive processes involved in producing and understanding linguistic communication
flashback - noun a transition (in literary or theatrical works or films) to an earlier event or scene that interrupts the normal chronological development of the story
foil - noun anything that serves by contrast to call attention to another thing's good qualities
folk - noun people in general (often used in the plural); the traditional and typically anonymous music that is an expression of the life of people in a community; people descended from a common ancestor
tale - noun a trivial lie; a message that tells the particulars of an act or occurrence or course of events; presented in writing or drama or cinema or as a radio or television program
foreshadowing - adj. indistinctly prophetic; noun the act of providing vague advance indications; representing beforehand
free - adj. not literal; able to act at will; not hampered;
verse - noun a piece of poetry; a line of metrical text; literature in metrical form; verb familiarize through thorough study or experience; compose verses or put into verse
genre - noun a class of art (or artistic endeavor) having a characteristic form or technique; a kind of literary or artistic work; an expressive style of music; a style of expressing yourself in writing
gothic - adj. characterized by gloom and mystery and the grotesque; of or relating to the Goths; of or relating to the language of the ancient Goths; characteristic of the style of type commonly used for printing German; as if belonging to the Middle Ages; old-fashioned and unenlightened; noun a style of architecture developed in northern France that spread throughout Europe between the 12th and 16th centuries; characterized by slender vertical piers and counterbalancing buttresses and by vaulting and pointed arches; a heavy typeface in use from 15th to 18th centuries
tale - noun a trivial lie; a message that tells the particulars of an act or occurrence or course of events; presented in writing or drama or cinema or as a radio or television program
hyperbole - noun extravagant exaggeration
imagery - noun the ability to form mental images of things or events
implication - noun an accusation that brings into intimate and usually incriminating connection; a relation implicated by virtue of involvement or close connection (especially an incriminating involvement)
incongruity - noun the quality of disagreeing; being unsuitable and inappropriate
inference - noun the reasoning involved in drawing a conclusion or making a logical judgment on the basis of circumstantial evidence and prior conclusions rather than on the basis of direct observation
irony - noun incongruity between what might be expected and what actually occurs; a trope that involves incongruity between what is expected and what occurs; witty language used to convey insults or scorn
Thursday, January 29, 2015
Friday, January 23, 2015
Dickens Notes
When Dickens wrote, his neighbors would call the cops.
He would yell and scream and talk in the voice of his characters as he was getting to know them.
"I'm not really writing lyrics, I'm taking notes of this great concert inside my head."
Dickens was nuts, in a good way; a creative genius.
He makes the characters feel real; we can relate to them.
He writes about his own life experiences, making his work very comparable to our own lives.
Thursday, January 22, 2015
VOCABULARY #8
1. Circumlocution- (n.) an indirect way of expressing something; a style that involves indirect ways of expressing things

2. Classicism- (n.) a movement in literature and art during the 17th and 18th centuries in Europe that favored rationality and restraint and strict forms

3. Cliché- (n.) a trout or obvious remark

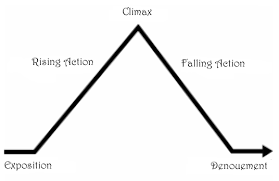
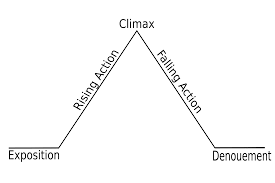
4. Climax- (n.) the decisive moment in a novel or play; arrangement of clauses in ascending order of forcefulness; the highest point of anything conceived of as growing or developing or unfolding
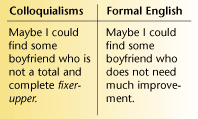
5. Colloquialism- (n.) characteristic of spoken or written communication that seeks to imitate informal speech
6. Comedy- (n.) light and humorous drama with a happy ending; a comic incident or series of incidents

7. Conflict- (n.) an open clash between two opposing groups (or individuals); an incompatibility of dates or events; opposition between two simultaneous but incompatible feelings; opposition in a work of drama or fiction between characters or forces (especially an opposition that motivates the development of the plot); the reference of an expression

8. Connotation- (n.) an idea or feeling that a word invokes in addition to its literal or primary meaning

9. Contrast- (n.) the act of distinguishing by comparing differences; the range of optical density and tone on a photographic negative or print (or the extent to which adjacent areas on a television screen differ in brightness); (v.) put in opposition to show or emphasize differences; to show differences when compared; be different

10. Denotation- (n.) the most direct or specific meaning of a word or expression; the class of objects that an expression refers to; the act of indicating or pointing out by name

11. Denouement- (n.) the final resolution of the main complication of a literary or dramatic work; the outcome of a complex sequence of events
12. Dialect- (n.) the usage or vocabulary that is characteristic of a specific group of people

13. Dialectics- (n.) a rationale for dialectic materialism based on change through the conflict of opposing forces
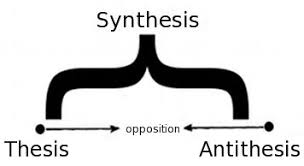
14. Dichotomy- (n.) being twofold; a classification into two opposed parts or subclasses

15. Diction- (n.) the manner in which something is expressed in words; the articulation of speech regarded from the point of view of its intelligibility to the audience

16. Didactic- (adj.) instructive (especially expressively)

17. Dogmatic- (adj.) characterized by assertion of unproved or unprovable principles; relating to or involving drama; of or pertaining to a characteristic of a doctrine or code of beliefs accepted as authoritative

18. Elegy- (n.) a mournful poem; a lament for the death

19. Epic- (n.) a long narrative poem telling of a hero's deeds

20. Epigram- (n.) a witty saying

2. Classicism- (n.) a movement in literature and art during the 17th and 18th centuries in Europe that favored rationality and restraint and strict forms
3. Cliché- (n.) a trout or obvious remark
4. Climax- (n.) the decisive moment in a novel or play; arrangement of clauses in ascending order of forcefulness; the highest point of anything conceived of as growing or developing or unfolding
5. Colloquialism- (n.) characteristic of spoken or written communication that seeks to imitate informal speech
6. Comedy- (n.) light and humorous drama with a happy ending; a comic incident or series of incidents
7. Conflict- (n.) an open clash between two opposing groups (or individuals); an incompatibility of dates or events; opposition between two simultaneous but incompatible feelings; opposition in a work of drama or fiction between characters or forces (especially an opposition that motivates the development of the plot); the reference of an expression
8. Connotation- (n.) an idea or feeling that a word invokes in addition to its literal or primary meaning
9. Contrast- (n.) the act of distinguishing by comparing differences; the range of optical density and tone on a photographic negative or print (or the extent to which adjacent areas on a television screen differ in brightness); (v.) put in opposition to show or emphasize differences; to show differences when compared; be different
10. Denotation- (n.) the most direct or specific meaning of a word or expression; the class of objects that an expression refers to; the act of indicating or pointing out by name
11. Denouement- (n.) the final resolution of the main complication of a literary or dramatic work; the outcome of a complex sequence of events
12. Dialect- (n.) the usage or vocabulary that is characteristic of a specific group of people
13. Dialectics- (n.) a rationale for dialectic materialism based on change through the conflict of opposing forces
14. Dichotomy- (n.) being twofold; a classification into two opposed parts or subclasses
15. Diction- (n.) the manner in which something is expressed in words; the articulation of speech regarded from the point of view of its intelligibility to the audience
16. Didactic- (adj.) instructive (especially expressively)
17. Dogmatic- (adj.) characterized by assertion of unproved or unprovable principles; relating to or involving drama; of or pertaining to a characteristic of a doctrine or code of beliefs accepted as authoritative
18. Elegy- (n.) a mournful poem; a lament for the death
19. Epic- (n.) a long narrative poem telling of a hero's deeds
20. Epigram- (n.) a witty saying
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)